|
|
|
|
A computer network refers to a collection of interconnected computers designed for communication and sharing data or resources. These networks enable computers to collaborate, share hardware and software resources, and exchange information efficiently.
In simple terms, a computer network consists of computers and peripheral devices that are linked together for data sharing and resource utilization. These networks allow computers to function both independently and collaboratively, with each computer referred to as a “node.” The connection can be established through cables, telephone lines, radio waves, or infrared light.
Advantages of Computer Networking
Some of the advantages of computer networking are as follows :
| Communication | People use networks to communicate with each other by exchanging messages and information. Computers connected to each other allow information to get transferred easily and quickly. |
| Sharing of hardware resource | Networking of computers enables users to share hardware resources like scanners, printers, etc. You may have noticed that your computer lab has more number of computers as compared to printers. This is because they are networked and share the printers. |
| Sharing of software | Software on a network can be shared with many people. People can run programs which are not installed on their own computers. Networks allow sharing of expensive software. |
| Preserving informaion | It is difficult to maintain regular backups on a number of standalone computers. When you keep backups on a central location, you have one place to look for the lost information. |
| Cost effectiveness | Sharing of resources results in reducing the additional cost of buying hardware and software. |
| Redundancy | A network reduces the need for hard copies of all documents. By sharing files over the network, the need for hard copies of resorts or any other information can be eliminated or greatly reduced. |
| Sharing documents quickly | The Internet provides a facility to instantly deliver soft copies from one computer to other computers throughout the world. |
| Updated data | Networking always helps us to deliver updated data and information at all nodes connected to it online. |
Key Components of a Computer Network
- Modem:

A device that modulates and demodulates signals, enabling communication between computers and the internet over telephone lines.
- Network Interface Card (NIC):
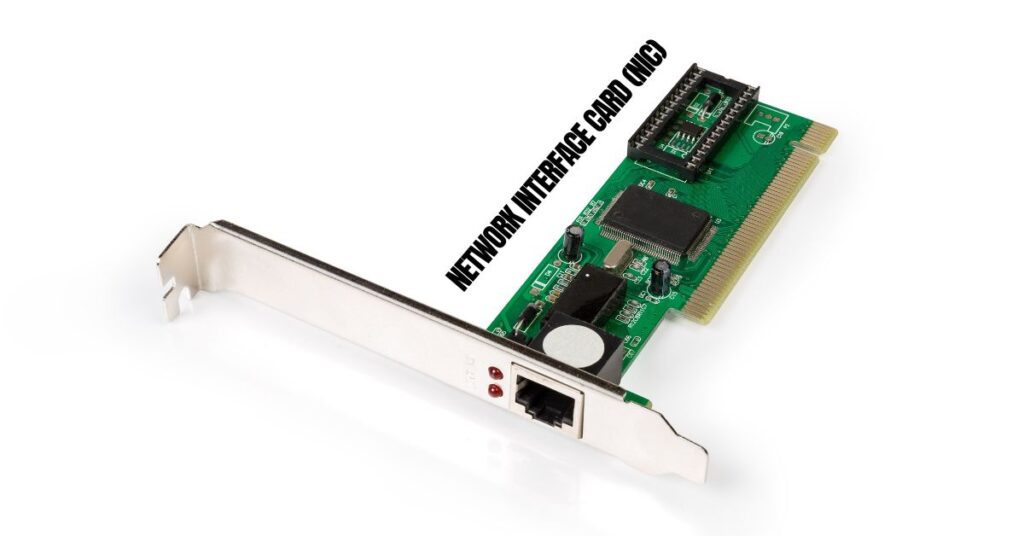

Also known as an Ethernet card, it enables computers to communicate over a network by providing a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address.
- Hub:
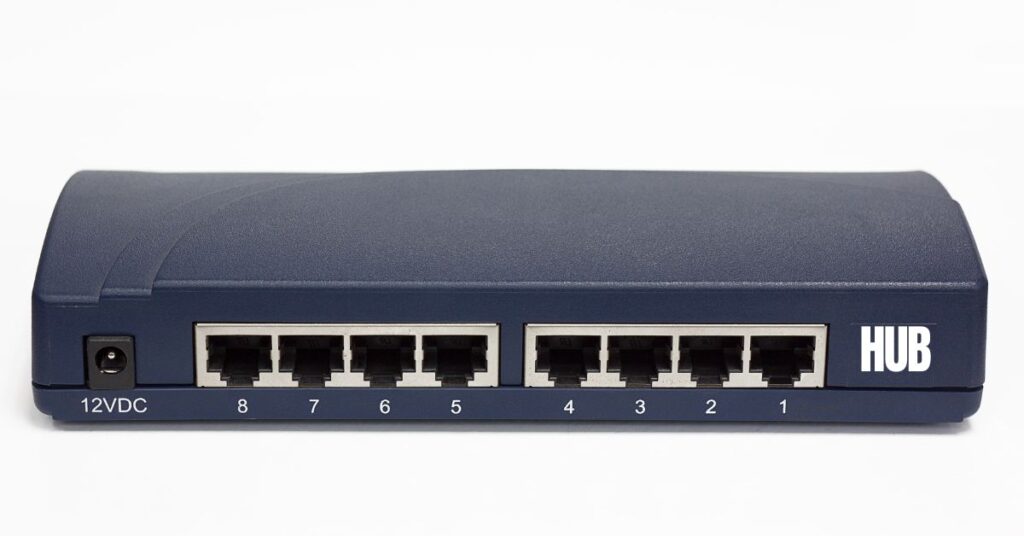

A device that connects multiple computers in a network, forwarding data packets to all connected devices.
- Switch:
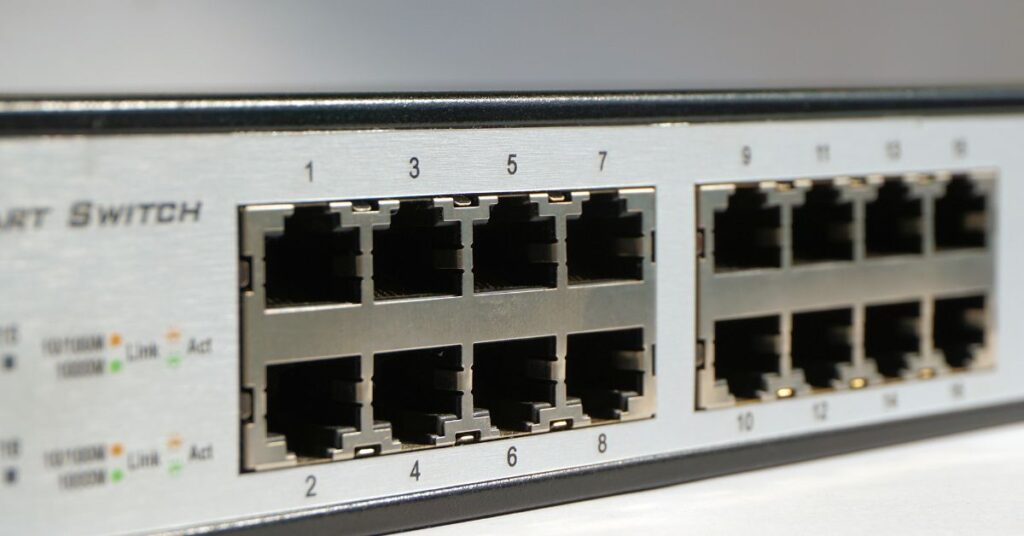

Similar to a hub but more efficient, a switch forwards data only to the intended recipient, improving network speed.
- Wireless Network Card:
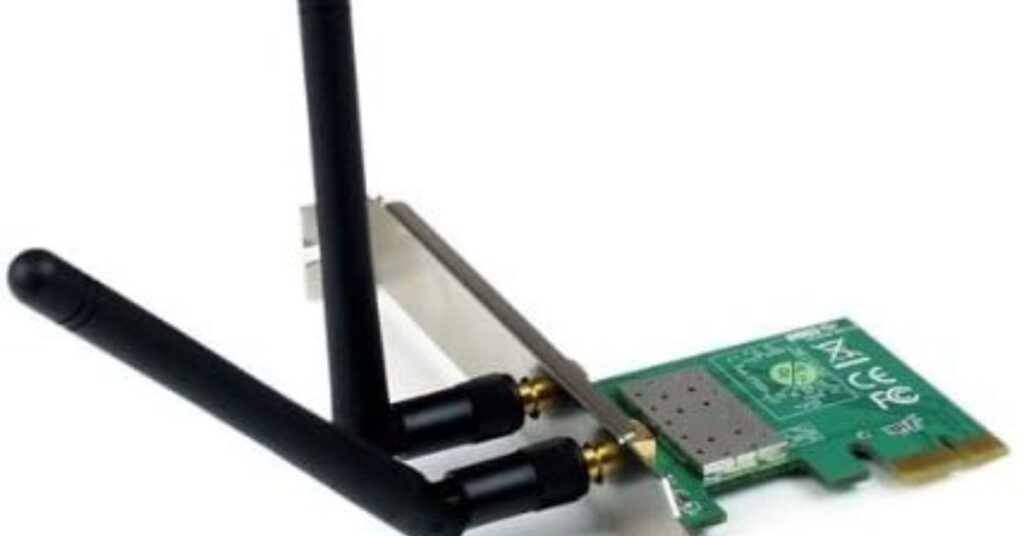

This card enables wireless communication, eliminating the need for physical cables.
- Router:
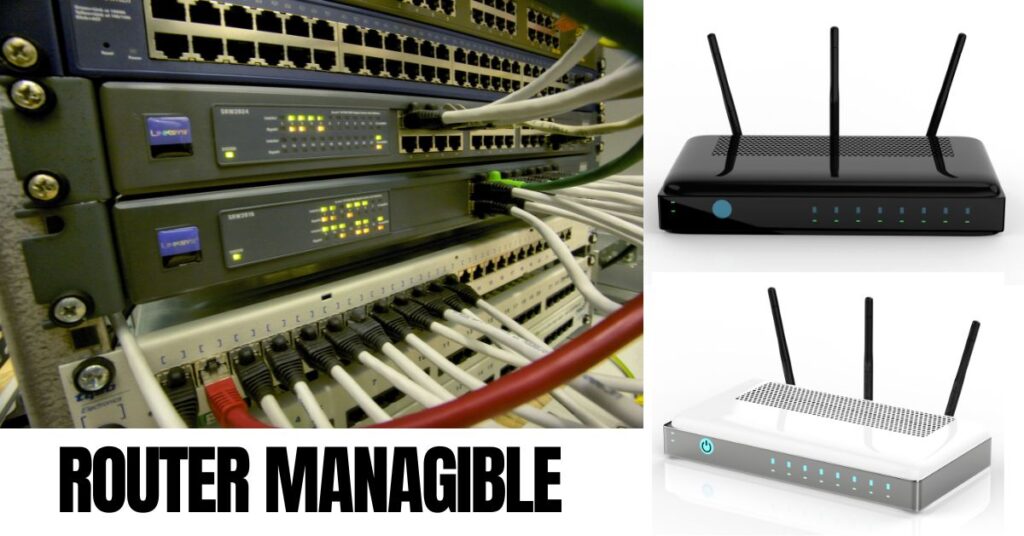

A device used to connect different networks, often combining wired and wireless connections to expand network coverage.
Types of Computer Networks
- Local Area Network (LAN):
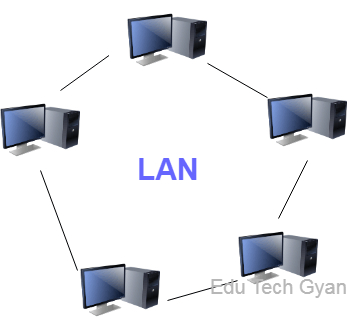
A small network connecting computers within a confined space like an office or building.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
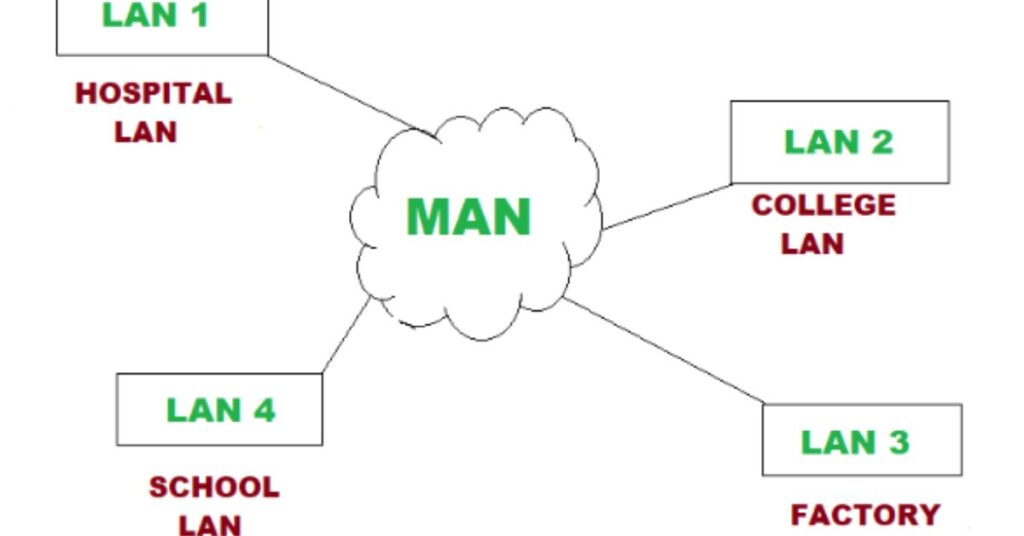
A larger network that spans a city or metropolitan area, often used by businesses with multiple branches.
- Wide Area Network (WAN):
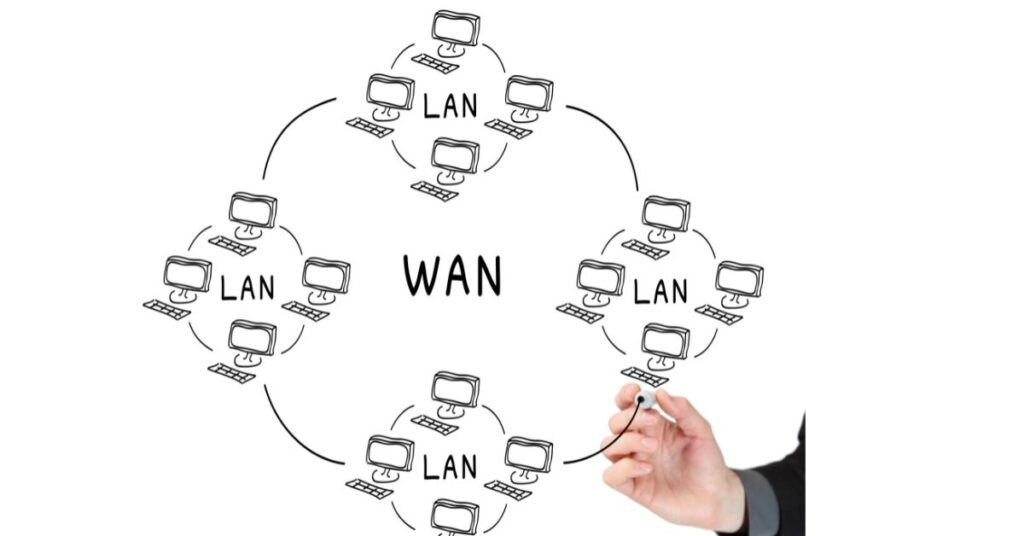
A global network connecting computers across cities, countries, or continents. The internet is the largest example of a WAN.
- Personal Area Network (PAN):
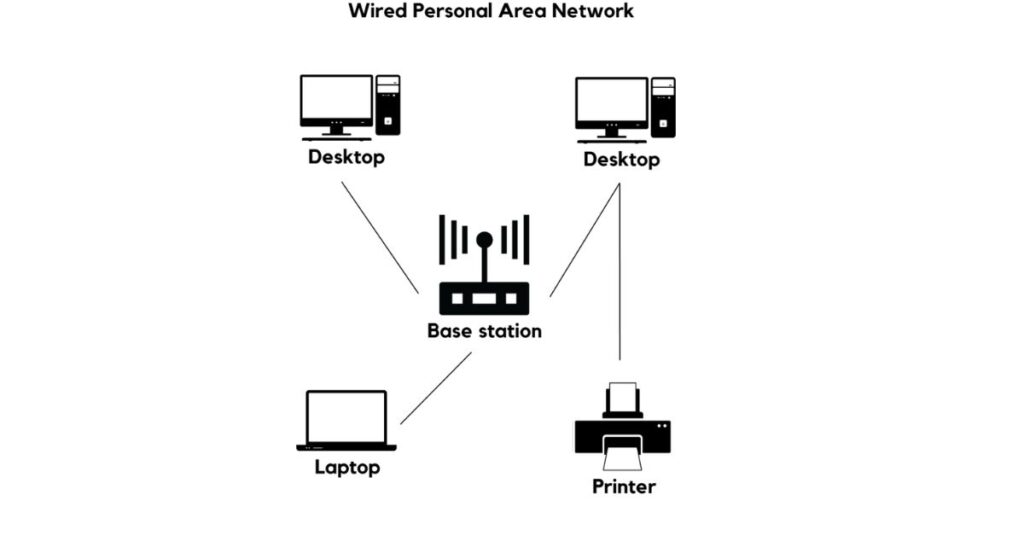
A small network centered around an individual, connecting devices like phones, laptops, and printers.
Network Architecture
- Client-Server Network:
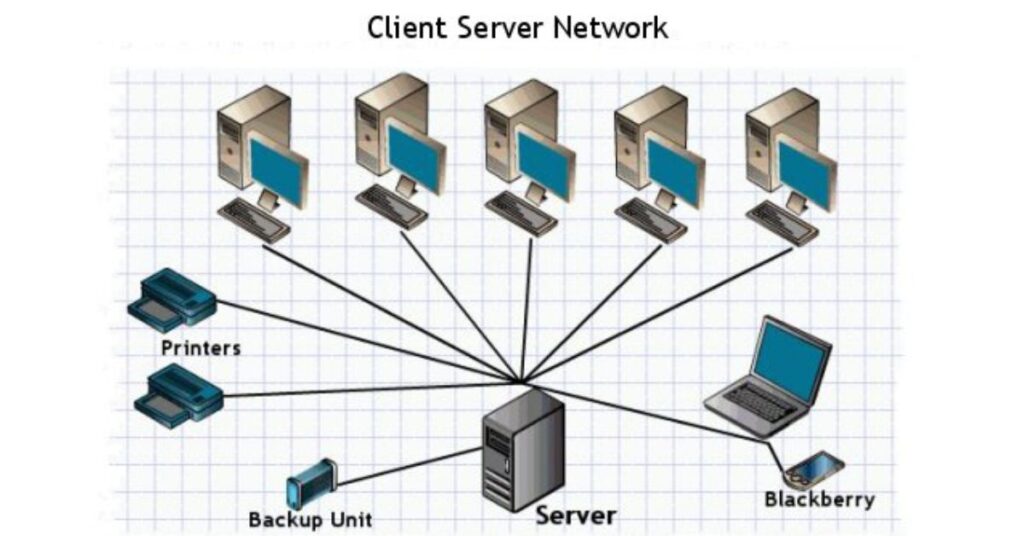
A centralized system where clients (computers) request resources from a server, which manages data access and hardware control.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network:
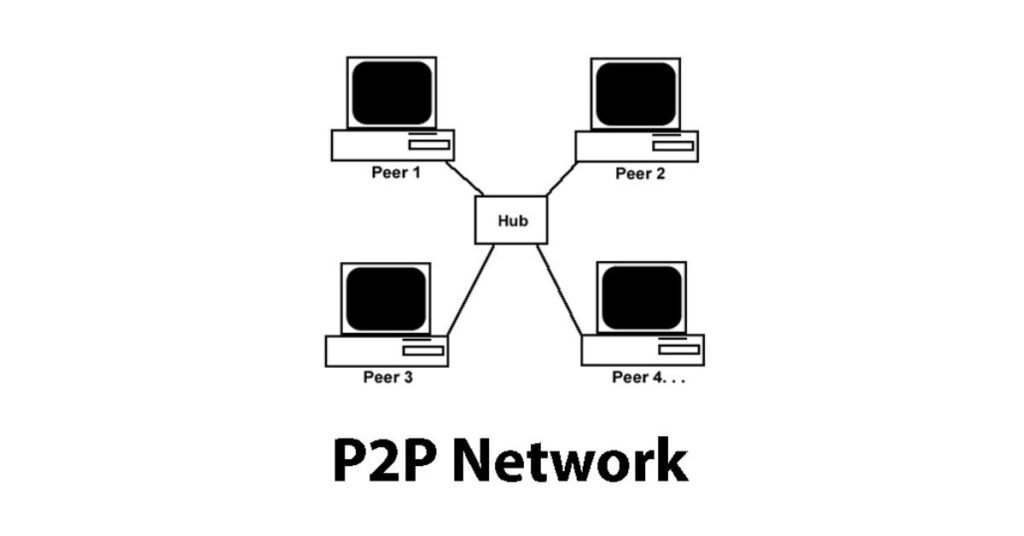
In this setup, computers have equal roles, acting both as clients and servers, sharing resources directly with each other.
Transmission Media
- Wired Media:
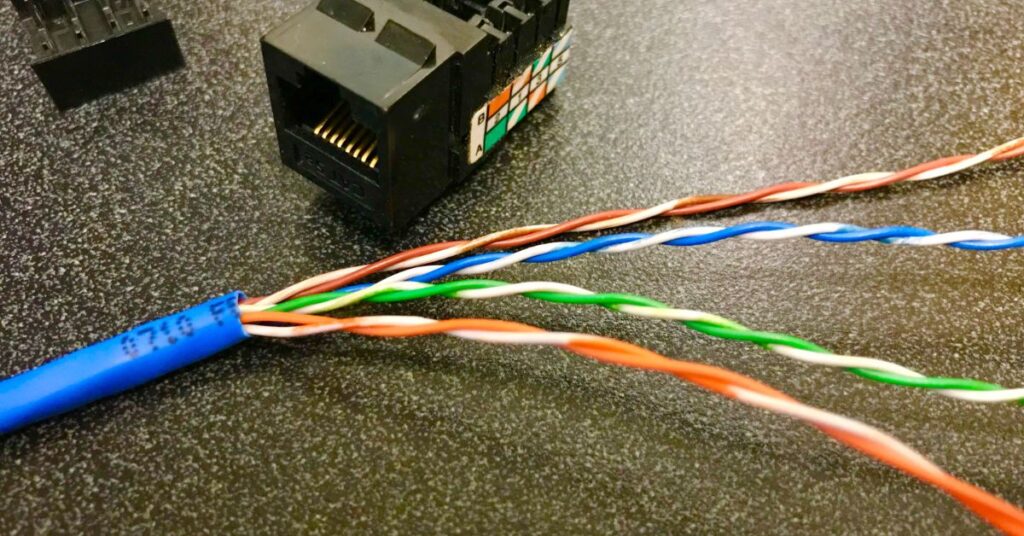

Data is transmitted using cables such as twisted pair, coaxial, or optical fiber. Twisted pair cables are the most commonly used in LANs.
- Wireless Media:

- Wireless transmission utilizes technologies like radio waves (e.g., Bluetooth and Wi-Fi) and infrared waves for short-range communication.
Network Topologies
- Bus Topology:
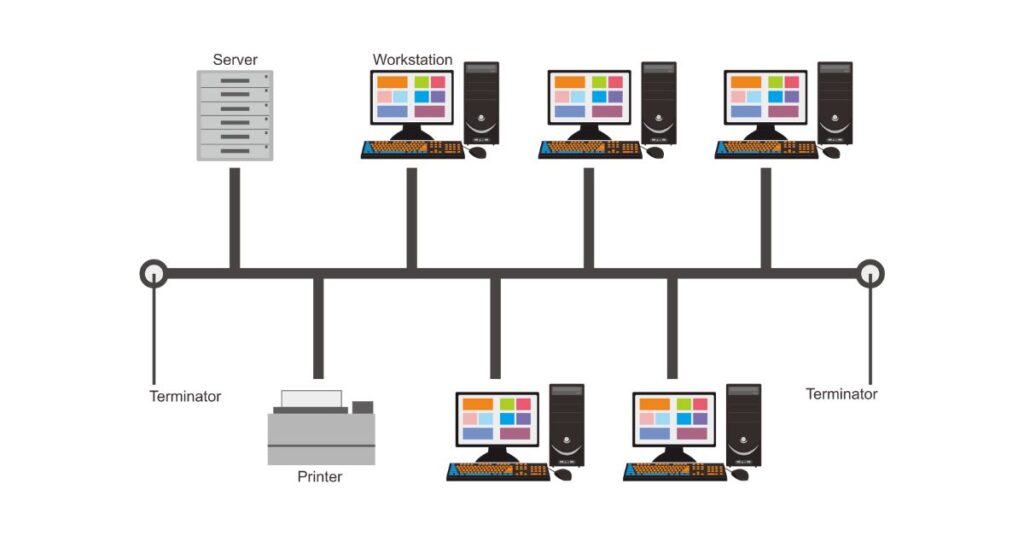
All devices are connected via a single communication line, with data traveling back and forth along the cable.
- Ring Topology:
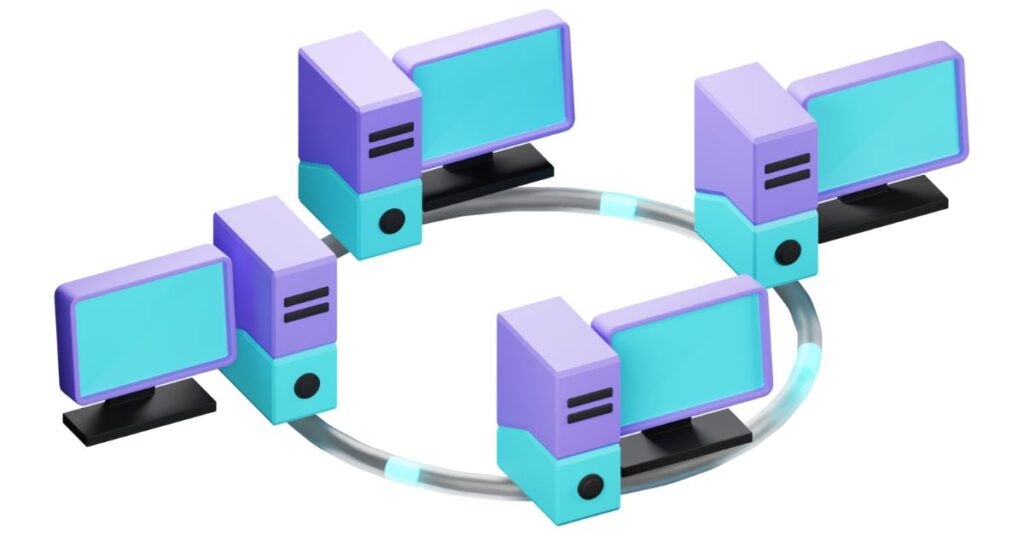
Devices are connected in a circular manner, with each device communicating with its adjacent device in a loop.
- Star Topology:
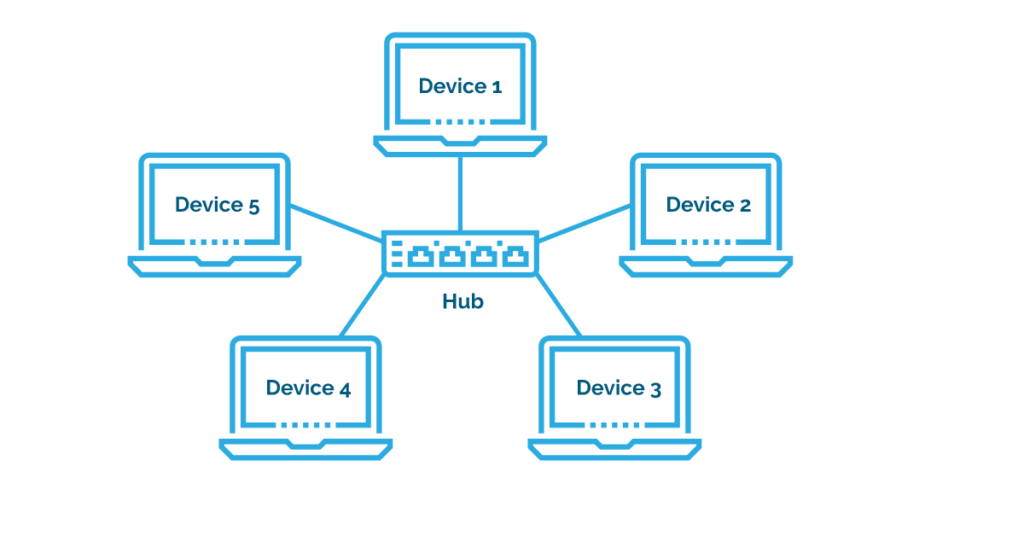
All devices are connected to a central hub or switch, ensuring centralized control and easy fault detection.
Conclusion:
Computer networks play a vital role in today’s digital world by enabling efficient communication, resource sharing, and data management. From small office networks (LAN) to global systems (WAN), they provide the backbone for modern technological infrastructure, ensuring seamless information flow across devices and users.
2 thoughts on “Understanding Computer Networks Step by Step With Images”